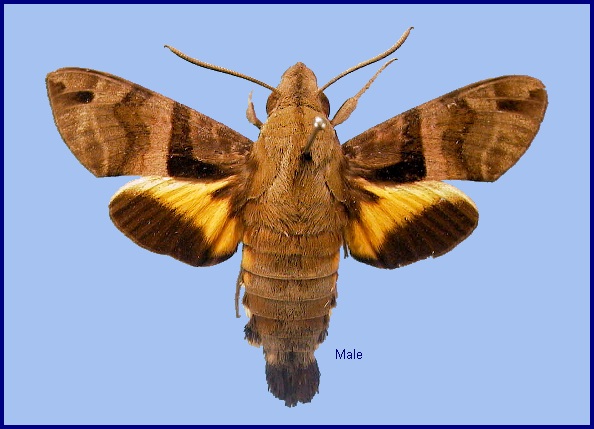
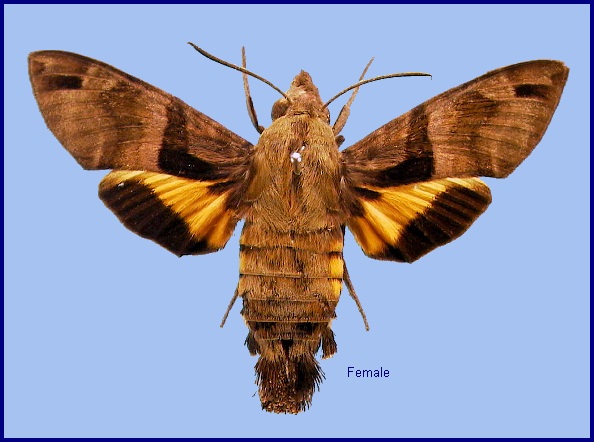

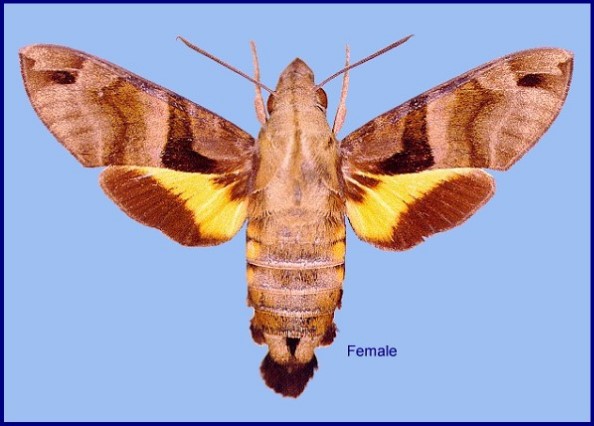
Macroglossa sitiene Walker, 1856, List Specimens lepid. Insects Colln Br. Mus. 8: 92. Type locality: [Bangladesh,] Silhet [Sylhet]; [Burma, Tenasserim,] Moulmein; North India; [South Africa, Natal,] Port Natal [Durban].
Synonym. Macroglossa nigrifasciata Butler, 1875.
Synonym. Macroglossa sinica Boisduval, 1875.
Synonym. Macroglossa sitiens Boisduval, 1875.
Synonym. Macroglossa orientalis Butler, 1876.
Synonym. Macroglossum chui Pan & Han, 2018.
[Further details on this species in Japan, as well as photos of many stages, can be found on Digital Moths of Japan.]
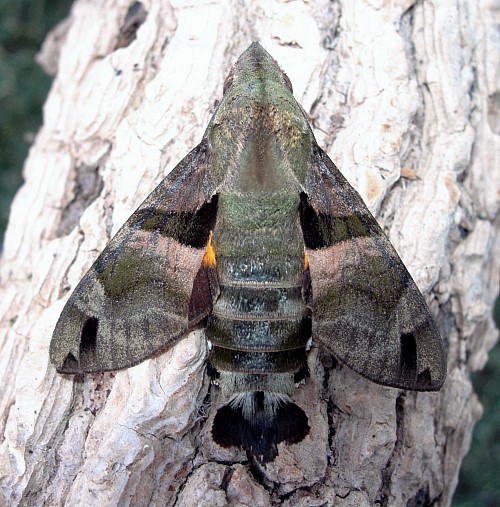
Wingspan: 46--56mm. Similar to Macroglossum heliophila, but body and forewing uppersides paler, clayish. Forewing upperside antemedian band very prominent, sharply dilated basad posteriorly; first and second discal lines curved as in Macroglossum heliophila, but the second not dilated distad posteriorly to vein M1. Both wings undersides more greyish distally than in Macroglossum heliophila, the lines of the hindwing prominent. Hindwing upperside yellow band deeper yellow than in Macroglossum heliophila, the edge of the black border less convex. Abdomen upperside with dorsal basal dots vestigial; seventh segment pale, with a very conspicuous black mesial patch; side tufts all prominently white-tipped. The anal fan in females is simple and held flat, that of the darker male is trident-shaped, and curved. Underside of palpus, middle of thorax, and mesial patches on the proximal abdominal sternites dirty grey, much less white than in Macroglossum heliophila.
In the male genitalia, uncus prism-shaped, rounded dorsally, furrowed ventrally, apex truncate. Gnathos rounded apically. Valve with stridulatory scales. Harpe almost straight, sharply pointed. Phallus with two processes: one broad, hook-shaped, dentate on the concave edge; the other very long and slender, horizontal; long internal rod broad, terminating in a long point.
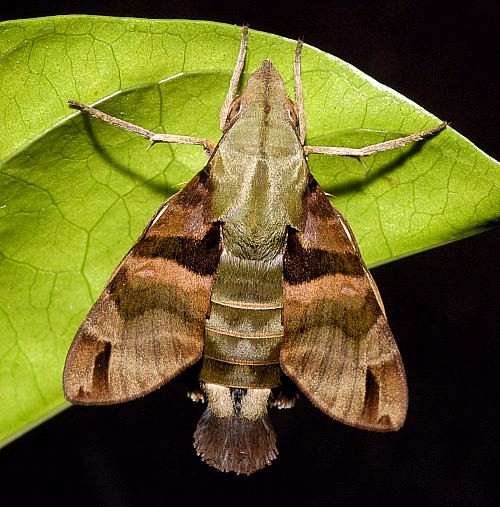



Attacted to Duranta erecta and Lantana camara blossom. Prefers flowers low down on bushes, flying very close to the ground when approaching. Active at temperatures as low as 6°C (Li, 1992).
China: v-vii (Hainan); vii (Guangdong; Guangxi); viii (Hainan); ix-x (Hong Kong); x (Guangdong; Hainan); xii (Hong Kong). Taiwan: vii (Tainan); vii-viii (Kaohsiung); x ([unstated locality]).
OVUM:
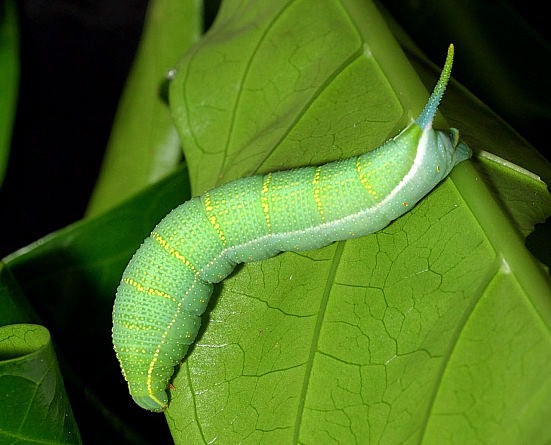
LARVA: Full-fed 53--58mm, width 8mm, horn 7.5mm. Polymorphic, with both green and brown forms. According to Bell & Scott (1937), in the final instar shape similar to others of the genus. Body dull, with an encircling row of small tubercles around each secondary ring. Horn long, slightly up-curved, tuberculate.
In colour, head green with a white subdorsal stripe and a white stripe separating face from cheek. Body with segments 2-4 green, remaining segments greyish-green. There is a dorso-lateral strip made up of whitish tubercles on segments 2-4, then narrow and bluish-grey until 11 and 12, where it is broader and whitish to base of horn. Tubercles on anterior secondary ring of each segment yellow, the rest whitish. Horn with basal two-fifths bluish-grey, sides violet near base, distal two-fifths green, shading to yellow at tip, tubercles black. True legs pale reddish-brown, basal segment with a black ring; prolegs ivory-yellow with a black basal band. Spiracles cream-coloured with a broad, brick-red central band (Bell & Scott, 1937).
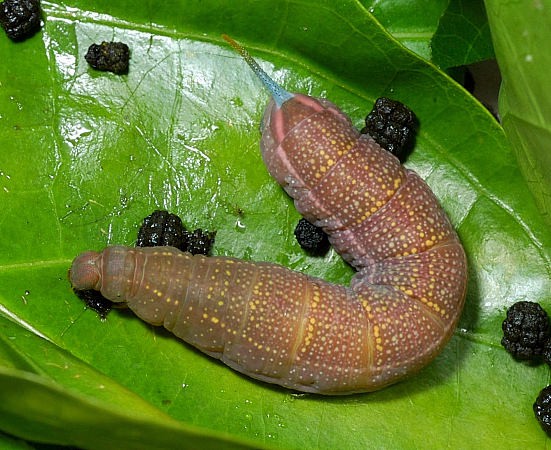





PUPA: 42mm, width 9mm. Colour of head and thorax dull greenish-grey, rest of body brownish-grey. Tongue-case with a median black stripe; wing-case mottled with black; body marked with dark dots and short stripes; spiracles black.
Shape similar to other pupae of the genus. Antenna, slightly longer than fore leg and reaching to about one-third of wing-case. Surface slightly shiny. Cremaster elongate-triangular, tip emarginate-truncate and slightly upturned, with a small conical tubercle at each lateral angle; dorsal surface smooth, ventral with two: curved longitudinal ridges down the middle and three channels, the central channel the broadest and shallowest (Bell & Scott, 1937).





Larval hostplants. Paederia foetida (Rubiaceae) in Hong Kong (Li, pers. comm. 2002) and Okinawa, Japan (Tanahara, 2015); Morinda umbellata as well as Paederia foetida farther north in China. Mainly on Morinda citrifolia [syn. Morinda tomentosa] in Bangkok, Thailand (Tony Pittaway, pers. obs.), as well as sometimes on Caladium bicolor and Duabanga grandiflora (DC.) Walp.
On Taiwan on Morinda citrifolia, Morinda umbellata, Serissa japonica [syn. Serissa serissoides], Paederia cavaleriei and Paederia foetida.
.


Braconidae: Meteorus stellatus Fujie, Shimizu & Maeto, 2021.
China: Yunnan (Hekou Yao Autonomous County); Guangdong (Dinghushan; Fengwan); Macau; Hong Kong (Kowloon); Guangxi (Baisha/Yangshuo, 150m); Hainan (??Manchyo; ??Secha; ??Taipinshi; Chengmai; Haikou; Wenchang; ??Yulinkang; Yinggen, 200m; Tongshi, 340m).
Taiwan: Tainan; Kaohsiung Hsien; Taipei Hsien (Yangmingshan); Nantou Hsien (Hueisun Forest; Puli); Pingtung Hsien (Kenting Botanical Garden).
Japan: Ryukyu Archipelago (Okinawa; Hateruma-jima (Kishida & Shirakawa, 1988)).
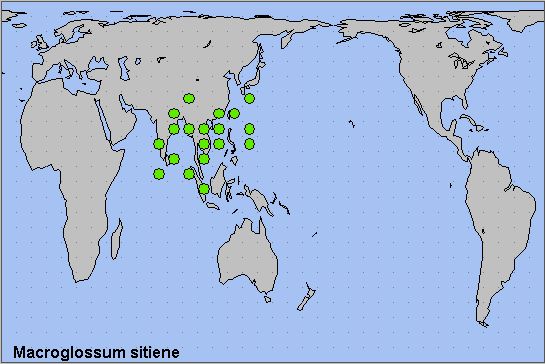
Sri Lanka, eastern India, Bhutan (Irungbam & Irungbam, 2019), Bangladesh, Burma/Myanmar, Thailand, southern China, Taiwan, southern Japan (Ryukyu Archipelago (Tanahara, 2015)), Vietnam, Malaysia (Peninsular) and Indonesia (Sumatra).
 Return to Sphingidae of the Eastern Palaearctic species list
Return to Sphingidae of the Eastern Palaearctic species list