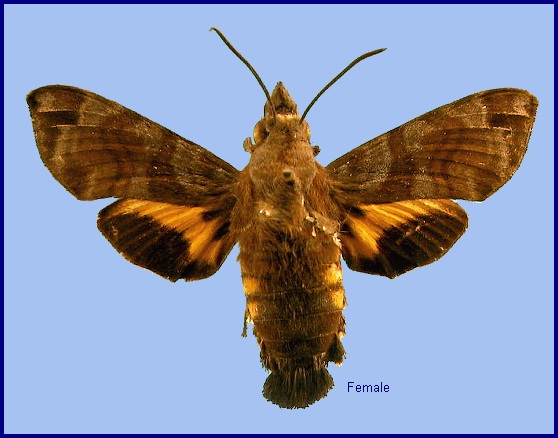
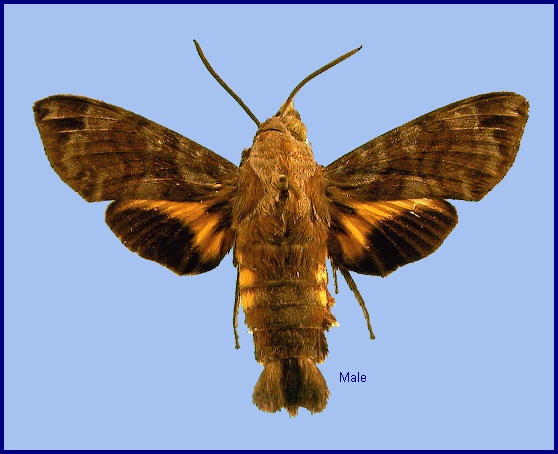
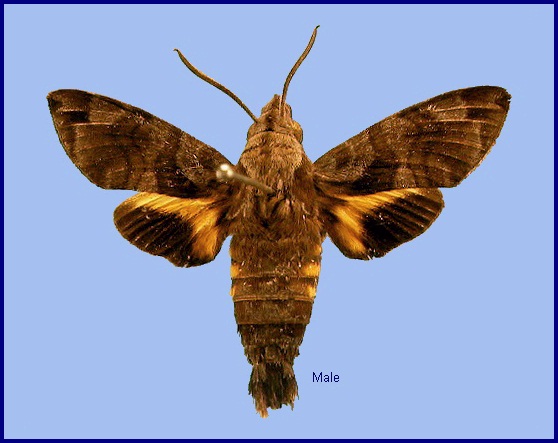



Macroglossum vicinum Jordan, 1923, Novitates Zoologicae 30: 189. Type locality: [India, Karnataka,] Canara [Kanara].
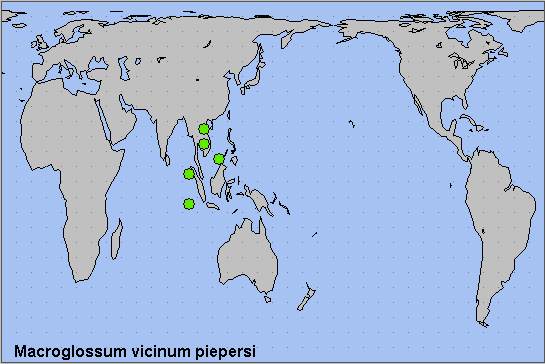
Note. The record of Macroglossum vicinum vicinum from China is suspect. As Macroglossum vicinum piepersi Dupont, 1941 occurs in Thailand, the individual from Xizang/Tibet, southern China, is probably Macroglossum vicinum piepersi. This requires further study. In fact, an example of the latter was captured at the Menglun Botanical Garden, Xishuangbanna, Yunnan, in December 2021 (Jiang, Xiong & Gan, 2022).
Wingspan: 40--48mm. In Macroglossum vicinum vicinum the size, colour and markings are similar to Macroglossum insipida insipida. Forewing as in Macroglossum insipida insipida, the markings the same but softer, the wing appearing less variegated. Hindwing median band slightly deeper yellow, the black marginal band less angulate below centre than is usually the case in Macroglossum insipida insipida. Underside of forewing uniformly dark cinnamon-rufous from base to terminal band, the basal area hardly at all shaded with darker brown, without yellow. Hindwing less extended yellow than in Macroglossum insipida insipida. Palpus less grey, being rather strongly shaded with walnut-brown. Grey margin of tegula less contrasting (Bell & Scott, 1937).
In the male genitalia of Macroglossum vicinum vicinum, harpe very different from that of Macroglossum insipida insipida, short, with a broadish subspatulate process, which is curved upwards and slightly away from inner surface of valve and bears numerous teeth at the rounded apex, at margin as well as on outer and inner surfaces. Phallus with a transverse apical process, dentate around its obtuse apex and along its proximal margin; the teeth near base of process rather long, conical, the teeth extending on to sheath, the large triangular tooth found on the sheath of Macroglossum insipida insipida absent; inside the sheath two daggers, one acuminate and dentate, the other spatulate and non-dentate (Bell & Scott, 1937).
In India, this species inhabits forests, and is on the wing during the rainy season. The moth has not been observed feeding nor coming to light (Bell & Scott, 1937). In Yunnan (China), this species mainly inhabits subtropical evergreen monsoon broad-leaved forest areas (Jiang, Xiong & Gan, 2022).
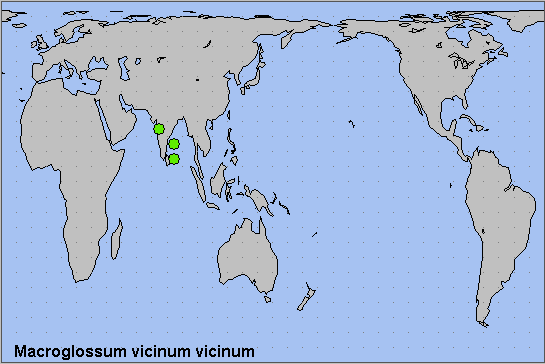
China: 13.xii.2021 (Menglun Botanical Garden, Xishuangbanna, Yunnan).
OVUM: In Macroglossum vicinum vicinum, pale honey-yellow, slightly oval (1.2 x 1.4mm), shiny and smooth (Bell & Scott, 1937).
LARVA: Full-fed 55mm, width 8mm, horn 6mm. According to Bell & Scott (1937), in Macroglossum vicinum vicinum the final instar head round, cutting-edge of mandible toothed. Surface of head dull and smooth. Body dull and smooth; horn straight, long, base stout, tapering evenly to a point, covered with small tubercles and rising from a conical tumidity.
In the green colour form, head green, suffused slightly with glaucous. With an obscure yellowish subdorsal stripe, and a similar stripe separating face from cheek. Labrum pale glassy-green; ligula similar, but sinus edges opaque white; basal segment of antenna green, other segments red; mandible green, tip narrowly dark reddish-brown. Body bright grass-green, dotted with white. There is a narrow yellow dorso-lateral stripe from segment 2 to near base of horn, missing on 5. White oblique lateral stripes are present on 5 to 11, obscure on 5, broad on 11, narrow on 12 to base of horn, the lower part of each stripe formed of short grey lines. Horn with dorsal surface dull green, sides of basal half china white with a bluish tinge, tip orange, the tubercles black on the green portion, white on the white portion and orange near the tip. Spiracles oval, flush, white suffused on each side of the central slit by reddish-brown (Bell & Scott, 1937).
There is also a dark-coloured form in which the head is green with pink reticulations and a brown subdorsal stripe. Segments 2 to 5 brown; remaining segments olive-brown, dorsum pinkish brown. There is an olive-brown dorsal stripe, and a dorso-lateral stripe that is yellow on 2 to 5, olive-brown on remaining segments. Brown oblique lateral stripes are present on 5 to 11, these edged below by olive-brown, and that on 11 becoming a white where it crosses 12 to base of horn. Latter fuscous with yellow tip (Bell & Scott, 1937).
There are also other forms intermediate in shade between the two described above.
In the resting position the head and anterior segments of the body are raised, the head held with the mouth-parts directed frontad, the true legs held against the venter.
PUPA: 32mm, width 8mm. In Macroglossum vicinum vicinum, bone-coloured, tongue-case rusty along its edge, tongue black. Head, thorax and wing-case tinged with greenish; tongue-case, legs and wing-case mottled plumbeous-grey. A dorsal stripe is present, which is narrow and black on thorax, diffuse green on abdomen. Pits on abdomen plumbeous; hind bevels of segments 8 to 10 pale chestnut, ante-spiracular ridges of 9 dark brown; venter of abdomen blotched with fuscous; spiracles black; cremaster chestnut (Bell & Scott, 1937).
Tongue-case projecting considerably frontad, semi-elliptical in profile; tip of tongue spatulate. Antenna reaching to nearly the middle of wing-case, fore leg slightly shorter. Surface shiny; head, thorax and wing-case smooth. Abdomen coarsely pitted with coalescent pits except on hind bevels of segments 8 to 10; front bevel of 9 with seven or eight irregular short ridges, the anterior ridge the most prominent, ridges becoming shorter and less, prominent backwards. There is a long channel reaching from the dorsal-lateral to ventro-lateral region in front of the anterior ridge. Spiracle of 2 as in pupa of M. insipida; remaining spiracles oval, flush, the central slit with narrow raised edges. Cremaster triangular, tip truncate, a short, tubercle at each lateral angle of the truncation venter hollowed longitudinally, a central keel at base dividing into two parallel arms which do not reach the tip, surface of cremaster smooth and shiny (Bell & Scott, 1937).
Larval hostplants. Macroglossum vicinum vicinum feeds on Chassalia curviflora (Rubiaceae) in India (Bell & Scott, 1937).
Unknown.
China: Xizang/Tibet (Zhaiyu; Zhangmu); Yunnan (Menglun Botanical Garden, Xishuangbanna, 500m).
Southern India, Sri Lanka and, maybe, southern China (Xizang/Tibet, Yunnan). The records from Xizang/Tibet, China, are probably not Macroglossum vicinum vicinum as there are no records from northern India. Therefore, as subspecies Macroglossum vicinum piepersi occurs in Thailand, all Macroglossum vicinum in southern China are probably Macroglossum vicinum piepersi, not Macroglossum vicinum vicinum. This was confirmed in 2021 by a capture of an individual of the latter at the Menglun Botanical Garden, Xishuangbanna, Yunnan Province (Jiang, Xiong & Gan, 2022).
 Return to Sphingidae of the Eastern Palaearctic species list
Return to Sphingidae of the Eastern Palaearctic species list