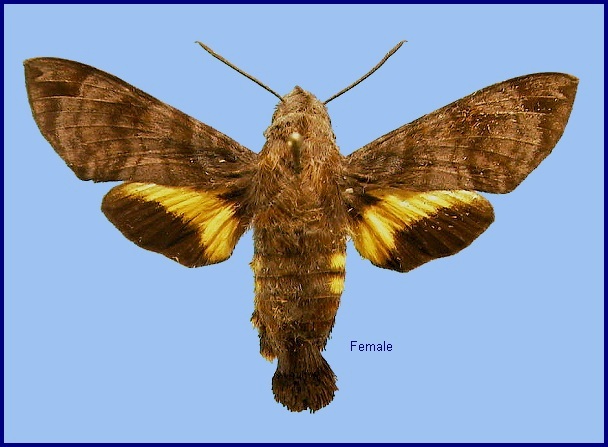
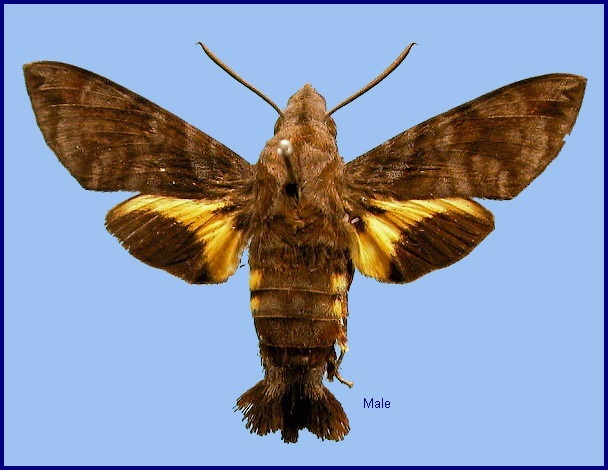
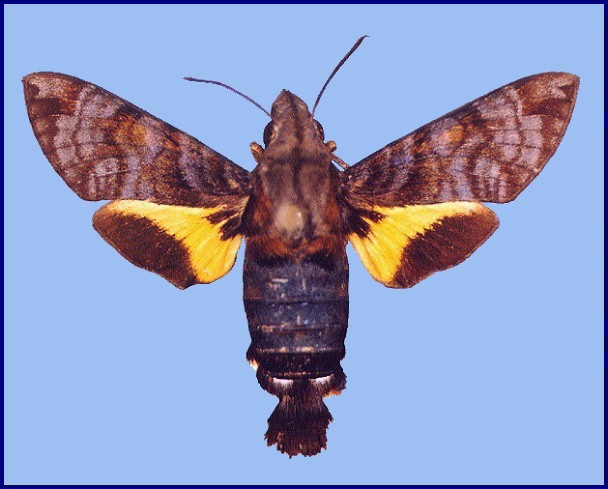



Macroglossum neotroglodytus Kitching & Cadiou, 2000, Hawkmoths of the world: 206. Type locality: India: Assam, Meghalaya, Shillong.
Synonym. Macroglossum troglodytus ferrea (Mell, 1922).
[Further details on this species in Japan, as well as photos of many stages, can be found on Digital Moths of Japan.]
The forewings have a beautiful, iridescent violet sheen to them in live individuals; this fades somewhat after death. Excluding the sheen, forewing upperside similar to Macroglossum insipida insipida, but ground colour rather uniform slate grey with a less prominent pattern of transverse bands and lines, giving the overall impression of a more sombre moth.
In the male genitalia, uncus narrower than in Macroglossum insipida insipida. Gnathos apically broader than in Macroglossum insipida insipida. Harpe bifurcate (a condition otherwise seen only in Macroglossum pyrrhosticta); upper lobe spatulate and flattened, with a convex dorsal surface and a convex ventral surface, and armed with short teeth along its broadly rounded outer edge; ventral lobe globular and covered in long, pinaculate setae. Vesica with two large cornuti; dorsal cornutus long, narrow and directed anteriorly toward the left side of the long axis of the phallus; ventral cornutus shorter, broader and directed anteriorly.
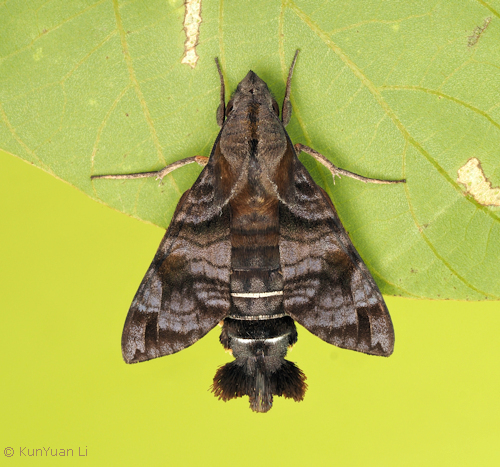
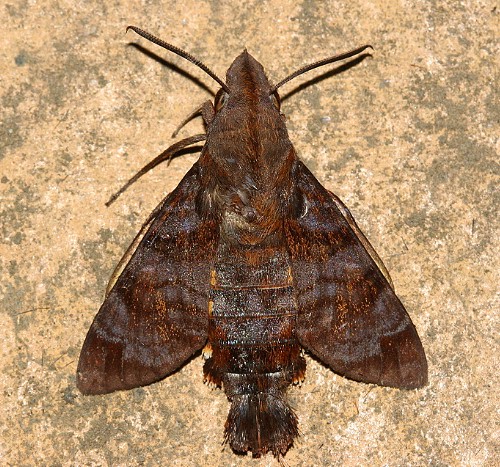
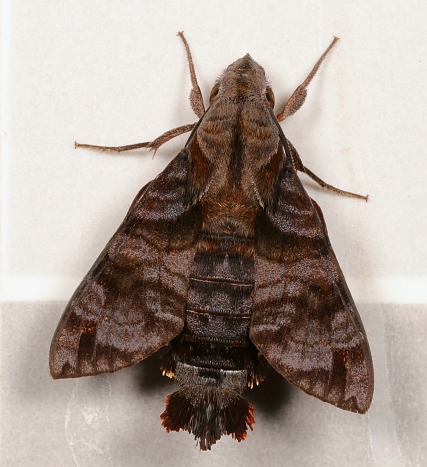



The moth is frequently on the wing in the morning and evening (Bell & Scott, 1937).
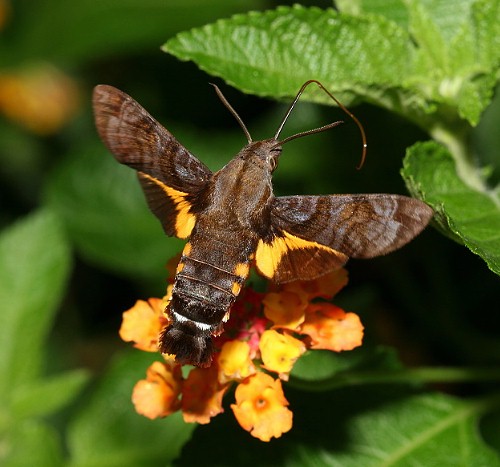
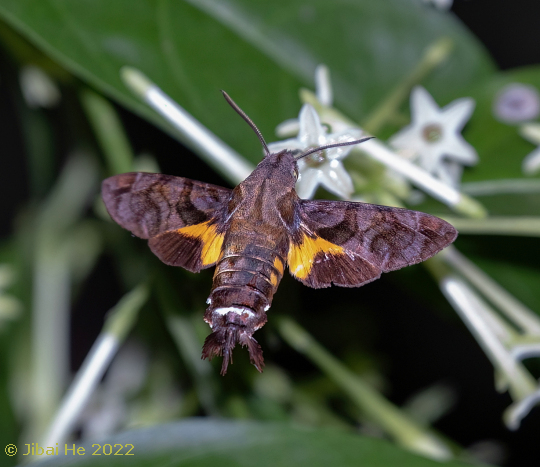
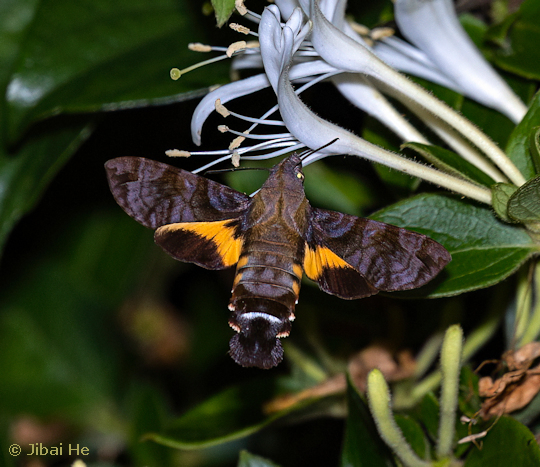



China: 19.v (Nanji Islands National Nature Reserve, Zhejiang); vii (Ya'an, Sichuan); xi (Simao/Pu'er, Yunnan; Jinghong, Yunnan). Taiwan: ii-iii (Taoyuan & Nantou Hsien), 3.vii-12.xii (Taiyuan & Nantou Hsien). Japan: 26.v (Ryukyu Archipelago).
OVUM: Green, broadly oval, smooth and shiny (Bell & Scott, 1937).
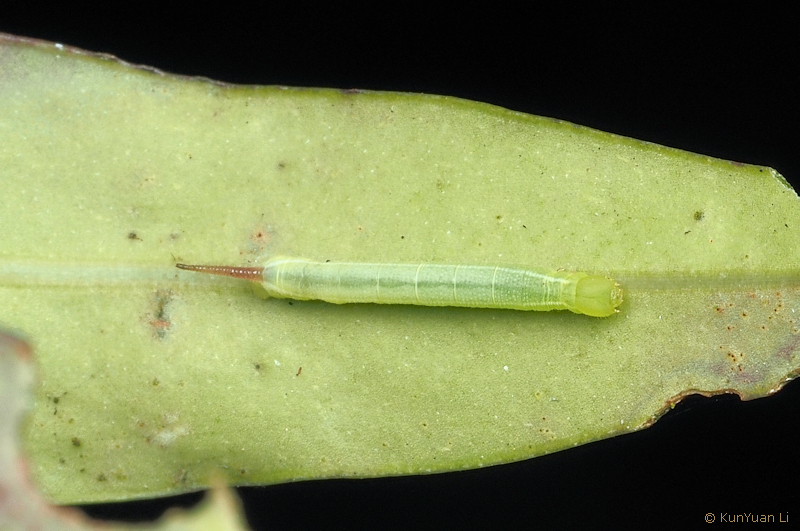
LARVA: Full-fed 50mm, width 6 mm. According to Bell & Scott (1937), in the first instar yellow when first hatched, green after feeding; horn black. In the second instar the basic body colour is green, the horn black. The third instar is also basically green, with dorsum dotted white. There is a whitish dorso-lateral stripe from segment 2 to horn. In the fourth instar head green with a darker green subdorsal stripe; body green dotted with yellow, bearing a darker green dorsal stripe and a whitish dorso-lateral stripe. There are seven dark green oblique lateral stripes. The horn is tuberculate, black, with yellow tip.
In the fifth instar, head with surface moderately shiny. Horn long, straight, with dull and smooth surface. Body dull and smooth except for a transverse row of small tubercles along each secondary ring in the dorsal area (Bell & Scott, 1937).
In colour, head green with a whitish subdorsal stripe. Body green, dorsal tubercles white. There is a dark green dorsal stripe from segment 4 to base of horn, flanked on each side by a white stripe. A yellow dorso-lateral stripe is also present from segment 2 to base of horn, and there are seven dark green oblique lateral stripes. Horn purple, tip yellow; true legs and prolegs reddish; anal flap edged with yellow. Spiracles reddish (Bell & Scott, 1937).
There is also a dark-coloured form in which the head is purple, subdorsal stripes paler purple, the body brown, the dorsal tubercles purple, the dorso-lateral yellow stripe broken or wanting on segments 5 to 11. In this form the oblique lateral stripes are dark brown dotted with purple; horn dark purple, tip yellow. True legs orange; prolegs steel-blue, claspers purple. Spiracles yellow (Bell & Scott, 1937).
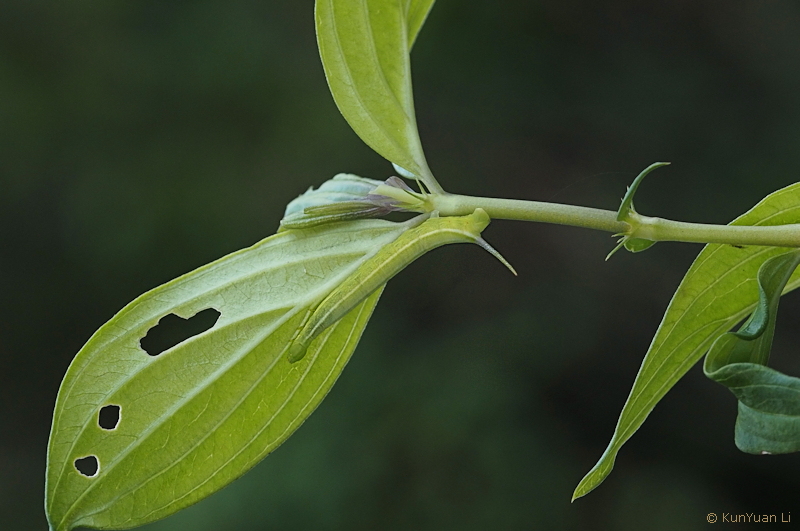
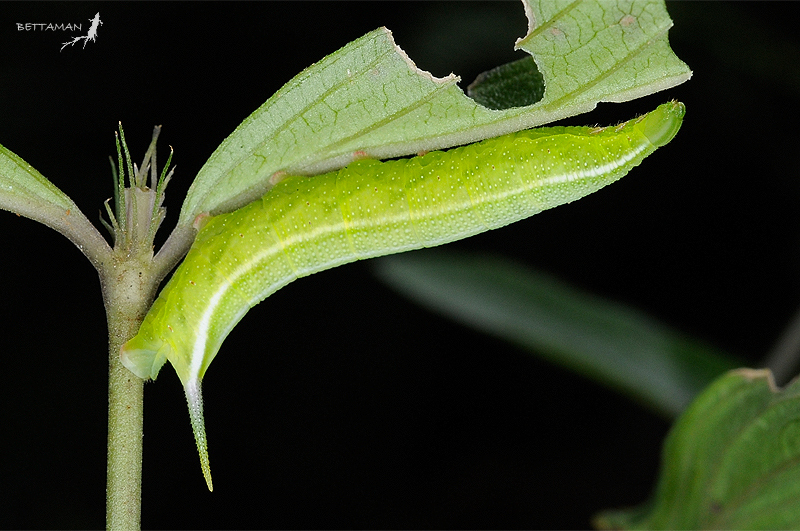





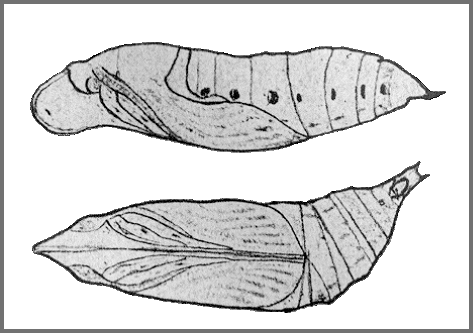
PUPA: Shape and surface as in other Macroglossine pupae. Colour of head and abdomen yellow, thorax greenish. Spiracles black.



Larval hostplants. Various Rubiaceae. In China recorded from Leptodermis at Kunming, Yunnan (ZhenBang Xu, pers. comm. 2023), and from Hedyotis caudatifolia and Dimetia hedyotidea [syn. Oldenlandia hedyotidea, Hedyotis hedyotidea] (DC.) T. C. Hsu in Guangdong, China (KunYuan Li, pers. comm. 2024). On Okinawa, Japan, from Scleromitrion diffusum (Willd.) R. J. Wang [syn. Hedyotis diffusa, Oldenlandia diffusa], a well-known Chinese medicinal herb (Tanahara & Tanahara, 2001). In India from Hedyotis uncinella Hook. & Arn. and Hedyotis scandens Roxb. (Bell & Scott, 1937).
On Paederia foetida in Taiwan (ShiPher Wu, pers. comm. 2012), as well as Oldenlandia corymbosa [syn. Hedyotis corymbosa], Dimetia hedyotidea, Richardia scabra, Serissa japonica [syn. Serissa serissoides] and Spermacoce alata [syn. Spermacoce latifolia].
China: Zhejiang (Nanji Islands National Nature Reserve, Wenzhou); Sichuan (Ya'an); Yunnan (Simao/Pu'er; Jinghong; Kunming); Guangxi (Guilin); Guangdong; Hong Kong.
Taiwan: Taipei Hsien (Zhinangong; Botanical Gardens; Shiding; Wulai); Taoyuan Hsien (Fuxing; Xinfeng); Nantou Hsien (Lianhuachi; Xiaofengkou, 3002m; Guandaoxi; Guandaoshan; Dongpu, 1200m); Yilan Hsien (Fushan); Taichung Hsien (Anmashan; Guguan); Hualien Hsien (Fuyuan); Kaohsiung Hsien (Neipu; Liangshan); Taitung Hsien (Lanyu).
Japan: Ryukyu Archipelago (Okinawa).
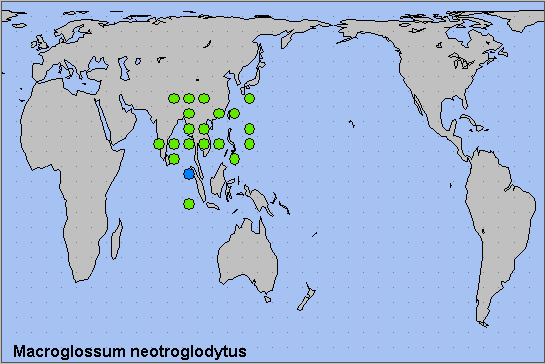
Sri Lanka, southern and northeastern India, Nepal, Bhutan (Irungbam & Irungbam, 2019), southern China (appears to be spreading north from Hong Kong), Ryukyu Archipelago, Japan (Tanahara & Tanahara, 2001), Taiwan, Thailand, Vietnam (Le & Vu, 2024), Malaysia (Peninsular), Indonesia (Sumatra, Java, Sulawesi) and the Philippines.
 Return to Sphingidae of the Eastern Palaearctic species list
Return to Sphingidae of the Eastern Palaearctic species list