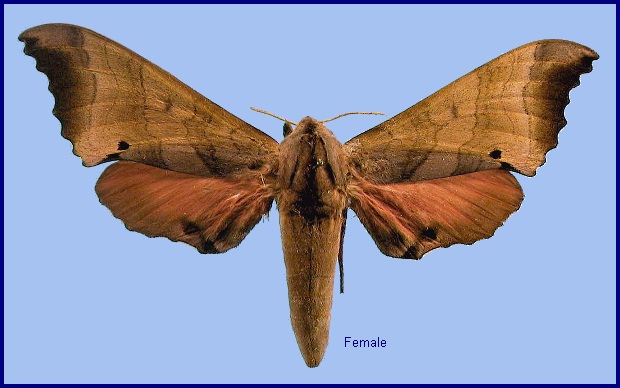

Smerinthus complacens Walker, [1865], List Specimens lepid. Insects Colln Br. Mus. 31: 40. Type locality: China, [Fujian,] Amoy [Xiamen].
Synonym. Marumba complacens circumcincta Eitschberger, 2012, Neue Entomologische Nachrichten 68: 62.
Synonym. Marumba complacens kernbachi Eitschberger & Hoa Binh Ngguyen, 2012, Neue Entomologische Nachrichten 68: 65.
Synonym. Marumba omeii Clark, 1936, Proceedings of the New England Zoological Club 15: 82-83.
Note. Marumba gaschkewitschii is currently divided into four subspecies: Marumba g. gaschkewitschii, Marumba g. complacens (Walker), Marumba g. carstanjeni (Staudinger), and Marumba g. gressitti Clark. However, the boundaries between these are not clear-cut, particularly within China. Specimens matching two or more subspecies can be found in the same locality at the same time, for example, as was observed at Yangling (17.vii.1995) and 30km north of Huangling, Shaanxi (24.vii.1995) (Pittaway & Kitching, 2000).
Three former subspecies/species, namely Marumba g. echephron (Boisduval, [1875]), Marumba harutai Eitschberger & Ihle, 2012, and Marumba g. irata Joicey & Kaye, 1917, are now considered to be distinct species (Eitschberger, 2012).
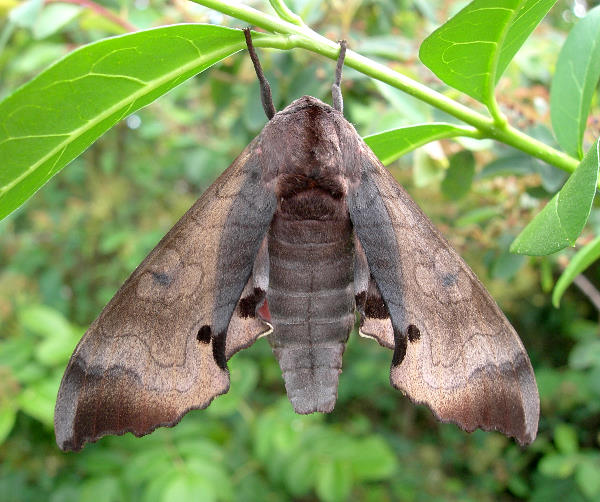
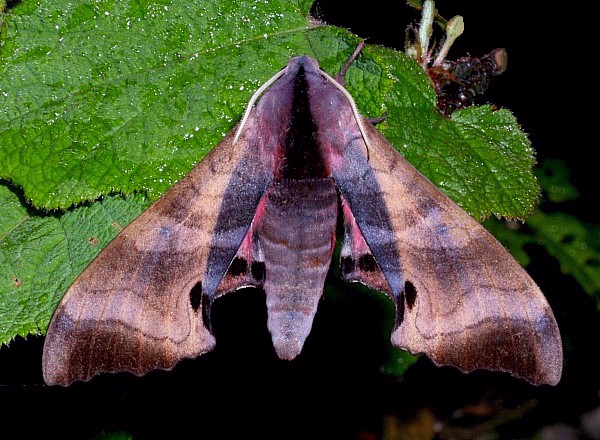


Marumba gaschkewitschii occurs in most habitats, including cities and orchards, and reaches over 2000m in Yunnan (Mell, 1935) and Nepal. Particularly common in montane forests rich in species of Prunus and Pyrus (Mell, 1935).
China: 15-28.ii (Guangdong); 28.ii-14.iii (Hong Kong); iv (Guangdong; Jiangxi); v-vi (Yunnan; Shanghai; Hong Kong; Zhejiang); vi (Hebei; Guangxi; Jiangxi); vii (Balin; Guangdong; Hailin; Zhejiang, 1500m; Sichuan; Xizang/Tibet); 17-24.vii (Shaanxi); viii (Fujian); 18.ix-14.x (Hong Kong).
Marumba gaschkewitschii s.l. has one to three generations a year. One is usual in Liaoning and Beijing, two in Ningxia, Hebei, Shandong, Jiangsu and Zhejiang; and three in Jiangxi (Chu et al., 1979). (Full-grown larvae were abundant around Beijing in late August 2003 (Pittaway, pers. obs. 2003).) Mell (1935) noted three to four generations (between 8.iii-5.x) in northern Guangdong and four to five generations (between 15.ii-2.xi) in southern Guangdong.
Kendrick (2002) states that this species is possibly trivoltine in Hong Kong, with adults recorded from late February to mid March, late May, and mid September to mid October.
OVUM: Oval (1.57 x 2.07mm). Initially a translucent pale jade green, but turning yellowish-green prior to hatching.

LARVA: Full-fed 75--83mm.
Newly hatched larvae are pale yellow with a round head and, in some, an orange tint to the horn. Only in the second instar does the characteristic triangular head appear, with the basic body colour turning gradually green. At this stage the final yellow oblique lateral lines and yellow body tubercles become more and more pronounced. The horn becomes more orange.
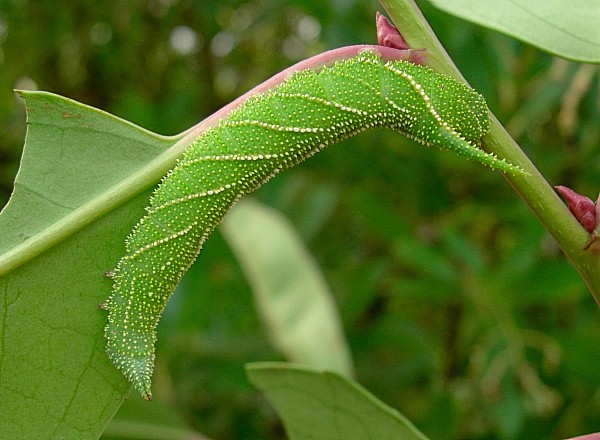





For the first few instars young larvae rest and feed stretched out along the midrib under a leaf. This behaviour makes them appear very elongate. Most larvae go through five or six instars. If the hostplant is of poor quality, some may even undergo seven.


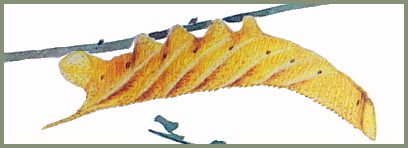

PUPA: 40--48mm. Reddish mahogany brown and glossy; tapering caudad from a blunt head and thorax. Head tuberculate, with two vertical, blunt, broad crests frontad. Proboscis not present, but replaced by a knob-like tubercle. Wings smooth, abdominal segments finely punctate. Spiracular ridges present on movable abdominal segments. Cremaster broadly conical, with a sharp point; tuberculate. Similar to that of Callambulyx tatarinovii, but head more rough and with two crest-like tubercles frontad, as found in most species of Marumba. Formed in an almost silk-free cell in the soil. The overwintering stage.



Larval hostplants. Prunus persica in Hong Kong.
Unknown.
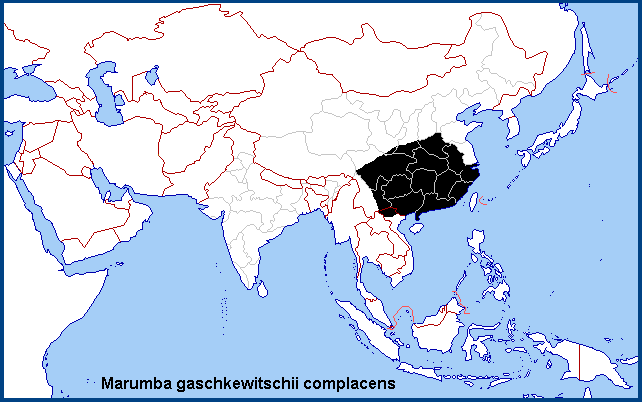
China: Central and southeastern China, from Ningxia, Gansu (Guan'egou Scenic Area) and Shaanxi (Yangling; Huangling; Xunyang, 1380m) south to Sichuan (Wolong National Nature Reserve; Pengshui; Emei Shan) and eastern Xizang/Tibet (Baxoi County; Langmai, Gonjo County (30°45'N, 98°52'E)), then east to Shanghai, Zhejiang (Tianmu Shan; Kuocang Mountain Nature Reserve) and Fujian (Guangze, 1200m) and south through Guangdong, Hong Kong and Guangxi (at low altitude) to Hainan Island (Sanya, Mt. Jianfengling).
The core distributions of the current four subspecies of Marumba gaschkewitschii are as follows:
Three former subspecies, namely Marumba gaschkewitschii echephron (Boisduval, [1875]), Marumba gaschkewitschii harutai Eitschberger & Ihle, 2012, and Marumba gaschkewitschii irata Joicey & Kaye, 1917, are now considered to be distinct species (Eitschberger, 2012).
Central and southeastern China, and northern Vietnam.
 Return to Sphingidae of the Eastern Palaearctic species list
Return to Sphingidae of the Eastern Palaearctic species list