

Macrosila inexacta Walker, 1856, List Specimens lepid. Insects Colln Br. Mus. 8: 208. Type locality: North India.
Synonym. Macrosila inexacta Walker, 1856.
Synonym. Meganoton khasianum Rothschild, 1894.
Synonym. Dolbina inexacta sinica Closs, 1914.
Synonym. Dolbina inexacta olivascens (Mell, 1922).
[Further details on this species in Japan, as well as photos of many stages, can be found on Digital Moths of Japan.]
Wingspan: 55--86mm. Forewing upperside with discal interspace sometimes pinkish grey between the discal cell and the hind margin: in male, distal margin almost straight, somewhat sinuate anterior to hind angle. Thorax, legs and wings undersides brown. Thorax underside meso- and metasternum with contrasting almost white scaling in mid-line. Tibiae and tips of tarsal segments conspicuous greyish white. Abdomen underside with very large black mesial patches; edges of sternites with almost white scaling contrasting with ground colour. Pilifer with a few bristles, but no scales, unlike Dolbina tancrei.
In the male genitalia, uncus flat, curved, short, membranous mesially to near apex, dilated before apex, then triangularly narrowed, shorter than in Dolbina tancrei. Gnathos shorter and more oblique than in other Dolbina, with lobes farther apart. Harpe with ventral process dorsally rounded-sinuate, the apex blunt; the dorsal process divided into a single, rounded, basal lobe, and a double distal lobe. Phallus with inner side with a small apical patch of spines apically; hook long. In the female genitalia, ostial cavity with triangular lobes at the edges of the cavity and anterior to it; the lobes about as long as the sinus between them.
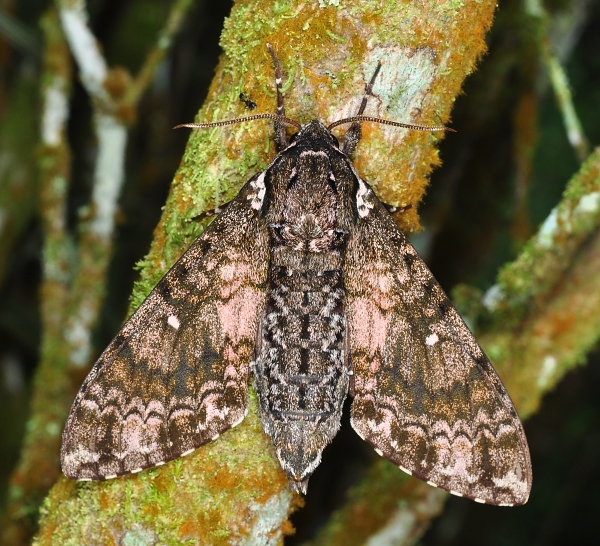
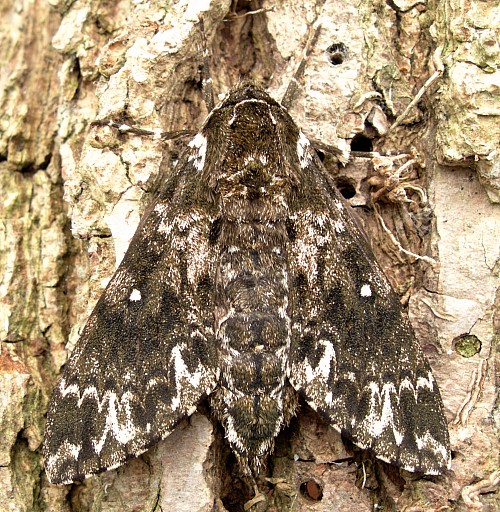
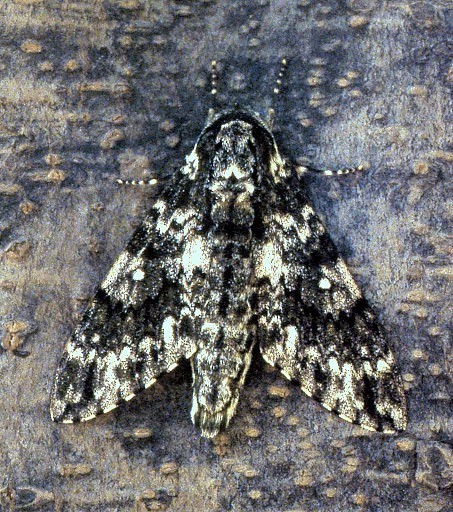




China: iii-iv (Guangdong; Yunnan); vi (Yunnan; Jiangxi); 20.vii (Shaanxi; Hubei); 25-30.vii (Yunnan); viii (Fujian; Zhejiang); ix (Shaanxi). *Japan: 20-21.iii (Ryukyu Archipelago); 9.x (Ryukyu Archipelago).
OVUM: Pale yellowish-green, almost spherical (2 x 1.25mm); surface smooth and shiny (Bell & Scott, 1937).
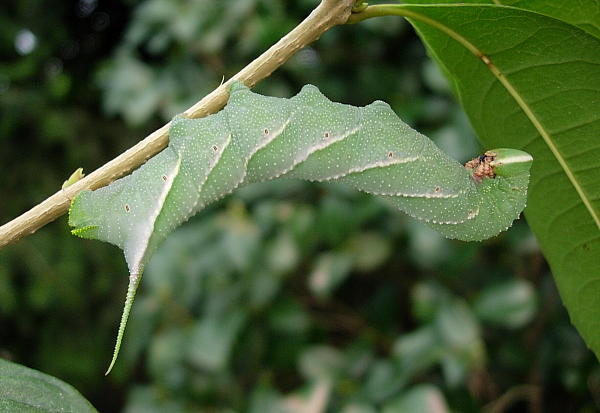
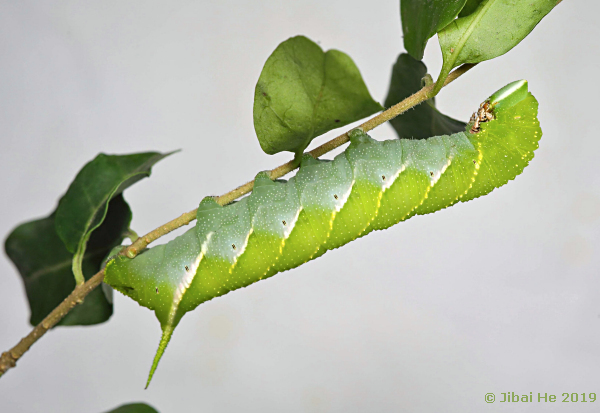
LARVA: Full-fed 52--70mm; width 11 mm.; horn 8.5 mm. According to Bell & Scott (1937), in the first instar, head round; body cylindrical; horn straight, long, tip bifid; anal flap tumid dorsally; colour pale yellow, horn reddish. In the second instar, head triangular, with a small tubercle at the vertex of each lobe. Horn straight, of medium length, with bifid tip. Colour of head green with a broad yellow cheek-stripe from vertex to base of antenna. Body grass-green, with a transverse row of pointed yellow tubercles on each secondary ring. There are large yellow dots on the subspiracular line of segments 2 to 4, and seven oblique lateral stripes formed of yellow tubercles, those on 6 and 11 better defined than the rest, that on 10 obsolescent. Horn dark red, tip black. True legs carmine ringed with white. In the third instar, tubercles more prominent, those on the oblique stripes multi-pointed. By the fourth instar, horn straight, tip shortly bifid. Head and body bluish-green, the lateral stripes white or yellow; horn green dotted with black, tip black.
In the final instar, head shortly triangular, a little higher than broad; true clypeus one-third length of head, each basal angle with a small tumidity; false clypeus with acute apex reaching to one-half length of head; labrum less than half length of clypeus; ligula as long as labrum. Surface shiny, set widely with low, minute tubercles. Body gently tapering frontad from segment 7. Horn long, straight, thick at base and tapering evenly to a blunt point. Surface dull; secondary rings of segments 2 to 4 raised into ridges on dorsum. Horn covered densely with small pointed tubercles, with large, round, closely-set tubercles on anal flap and claspers (Bell & Scott, 1937).
In colour, head bluish-green with a broad, pale yellow cheek-stripe from vertex to base of antenna; false clypeus dark green; labrum and ligula rust-coloured; basal segment of antenna dark brown, other segments rust-colour; mandible pale orange, tip black. Body rich bright green with a glaucous suffusion on dorsum. Oblique lateral stripes white or yellow, each crossing two segments and spreading into a more or less well-defined patch round the spiracles. Horn, anal flap and claspers green. Legs pale orange, base rose-coloured and a black ring on each segment; prolegs green. Spiracles reddish-brown with a white central slit widening slightly at top and bottom, the whole ringed with yellow, oval in shape and flush. In some specimens there are carmine patches round the spiracles, above the oblique stripes and at bases of true legs (Bell & Scott, 1937).
The larva is sluggish, except when looking for a place to pupate, and when at rest adopts the typical 'sphinx' posture. It rests without feeding for a couple of days before commencing to pupate, and while wandering about in search of a suitable place to burrow is more or less neutral coloured, losing all markings (Bell & Scott, 1937).
[A full, illustrated account of all the early stages of this species is given by Eitschberger & Hoa Binh Nguyen, 2015.]


PUPA: 48mm; breadth 14 mm. Chestnut to blackish-brown in colour, the bevels of the free abdominal segments paler; the spiracles brown. Ambulicine in shape, rather like that of Marumba dyras. Thickest in the middle; shoulders evenly rounded; dorsum of segment 2 very steeply inclined, rising nearly at right angles to the axis of the body, the dorsal line of 3 being nearly parallel with the axis. Tongue-case equal to fore leg, reaching to about the middle of wing-case; mid-leg longer, antenna slightly shorter than fore leg; no coxal piece. Surface shiny, irregularly corrugate on the head and thorax, elsewhere pitted with coarse shallow pits, except on wing-case. There are ante-spiracular ridges on segments 8 to 10, in the form of three short parallel ridges on each. Spiracle of 2 crescent-shaped; the remaining spiracles oval. Cremaster stout, ending in a short bifid tooth; the dorsal surface very rugose except for the tooth, which is smooth (Bell & Scott, 1937).
Pupation takes place in an ovoid cell, smooth inside but not lined with silk, and placed about 6 inches underground.


Larval hostplants. In China on Ligustrum robustum, Fraxinus and Osmanthus fragrans (Pittaway, pers. obs. 2004). Elsewhere, recorded form Olea, Lonicera, Ligustrum, Fraxinus and Osmanthus (Inoue, Kennett & Kitching, [1996] 1997).
On Olea paniculata R. Br. at Mussoorie, Uttarakhand, India (Bhuyan, Clark & Smetacek, 2019).
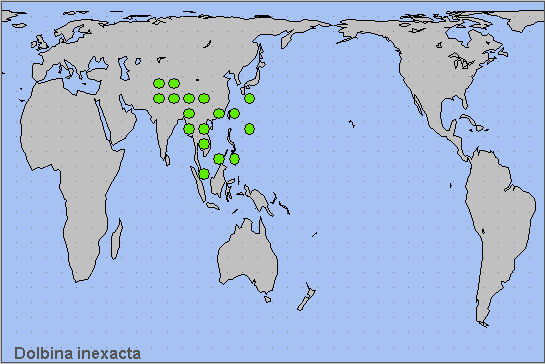
China: Shaanxi (Xi'an; Xunyang, 1380m); Anhui (Wangu Tower, Lu'an); Zhejiang (Siming Shan; Kuocang Mountain Nature Reserve); Hubei (Tiantangzhai, Luotian, 1729m); Sichuan (Kangding; Xiaolou; Chengdu); Chongqing (Fengjie; Chongqing); Yunnan (Yanmen; Laojun Shan, 2579m; Mengla County, Mt. Leigongyan, 2000m; Gaoligong Shan; Simao/Pu'er; Lijiang); south Xizang/Tibet (Bomi, 2750m); Hunan (Dayong; Cili); Jiangxi (Guling; Le'an); Fujian (Guangze, 1200m); Guangdong (Guangzhou).
Japan: ?Ryukyu Archipelago (Iriomote-jima; Ishigaki-jima).
From northern Pakistan (Rafi et al., 2014; Haxaire, Gujjar & Saeed, 2017), east through northern India (Pathania, Sunita Sharma & Gill, 2014; Bhuyan, Clark & Smetacek, 2019; Jatishwor Irungbam & Fric, 2021), Nepal and Bhutan (Irungbam & Irungbam, 2019), east across central and southern China, then through Burma/Myanmar, Thailand, Laos and Vietnam (Le & Vu, 2024) south to Peninsular Malaysia. Also Ishigaki-jima (Kishida, 1975) and Iriomote-jima (Ryukyu Archipelago), Japan, although these will probably turn out to be Dolbina formosana Matsumura, 1927 [More details given in An Identification Guide of Japanese Moths].
The populations in the western Ghats, southern India, have recently been described as a separate species, namely Dolbina manjunatha Haxaire & Melichar, 2013. That on Taiwan has been elevated to the status of a full species, namely Dolbina formosana Matsumura, 1927.
 Return to Sphingidae of the Eastern Palaearctic species list
Return to Sphingidae of the Eastern Palaearctic species list